How will AI impact automation? And what is Industry 4.0?
Since the invention of the first moving assembly line in 1913, automation has played a huge part in manufacturing across many sectors. Today, emerging technology like Artificial Intelligence (AI) has the potential to revolutionise the manufacturing industry completely.
Markets and Markets report that the AI market in manufacturing will reach 16.3 billion USD by 2027, increasing by 47.9% from 2022.

There’s no doubt that businesses should embrace new digital technologies by adopting AI into their workflows, but the question is – how can automation and AI work together?
AI in manufacturing
With problems such as supply chain issues and labour shortages, many companies are using digital transformation as a way of keeping up. By embracing AI-based technologies, companies like Siemens and General Motors are outperforming their competitors. Here are some of the ways AI is currently used in manufacturing:
- Predictive maintenance – avoiding equipment repairs by predicting when machines will break down
- Quality control – using ‘machine vision’ technology to spot flaws. Machine vision means the equipment can essentially see what it’s doing
- Robotics – as well as being able to perform monotonous tasks, robots can now also react to changes in input given by people and the environment
- Optimise production processes – using machine learning algorithms, businesses can analyse data from their operations to find ways to increase efficiency
According to a McKinsey survey, some of the results companies using AI have reported:
- 30-50% decrease in machine downtime
- 15-30% increase in labour productivity
- 10-20% reduction in the cost of quality
- 10-30% increase in output
AI vs. automation
Right now, the focus should be on how automation and AI can work together to improve efficiency, rather than AI taking over completely.
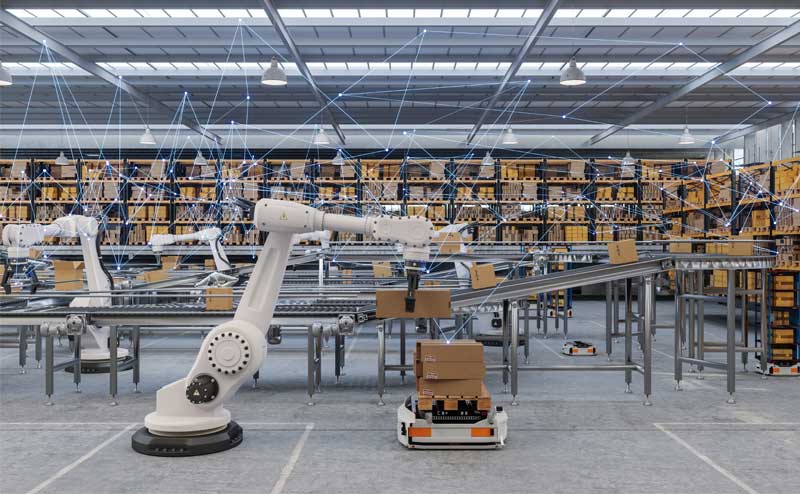

A good example is predictive maintenance, labelled by McKinsey as AI’s most significant tool in manufacturing.
Predictive maintenance uses AI technology to capture data and detect potential problems with equipment. This information is then used to predict and prevent unplanned machine breakdowns, significantly reducing costs and allowing the production line to continue to run. It also helps improve safety, as issues can be fixed before a dangerous malfunction occurs.
The AI side of this can work in a number of ways. It can take historical data and machine specifications and use that information to extrapolate into the future.

AI can also run simulations based on how real-world conditions might affect your machinery and learn from previous predictions to become more accurate over time.
What is Industry 4.0?
Closely related to the use of AI in manufacturing is the concept of Industry 4.0. Starting in the mid-2010s, Industry 4.0 is another name for the Fourth Industrial Revolution. This refers to the switch towards digitalisation in manufacturing.

Following on from the third revolution, during which computers and automation were adopted, businesses are now using new technologies such as AI, machine learning and the Internet of Things throughout their operations.
By using cloud technology, virtual reality, additive manufacturing (i.e. 3D printing) and other powerful tools, manufacturers are seeing huge increases in efficiency. Technology is only part of picture though. Businesses need to ensure their workforces are trained to use those new tools.
As we move through Industry 4.0, it’s clear that innovative technology like AI will continue to revolutionise manufacturing. To keep up with competitors, businesses should look to ways their current processes (particularly those that use automation) can be enhanced further with artificial intelligence.